Digital Pathways: From Clicks to Progress
On Monday, August 12, 2024, the world took a moment to spotlight its greatest asset—the over 1.2 billion youth and their role in advancing global development.
This year's theme, "From Clicks to Progress: Youth Digital Pathways for Sustainable Development," recognises that without youth-led innovative solutions, the efforts to meet global goals for peaceful, fair, and inclusive societies will yield little gains.
With this global theme comes the local concern: “How do we address the situation when many youths remain disconnected from the internet, particularly in developing countries?”
At the global level, digital innovations have reshaped every facet of corporate and public life, bringing with it new opportunities for communities and livelihoods.
Across countries, the level of digital access and utilisation among their youth, the digital natives, could influence their development.
Yet there are disparities in digital adoption rates between youths in advanced economies and those in developing countries.
Clicks: Digital Barriers
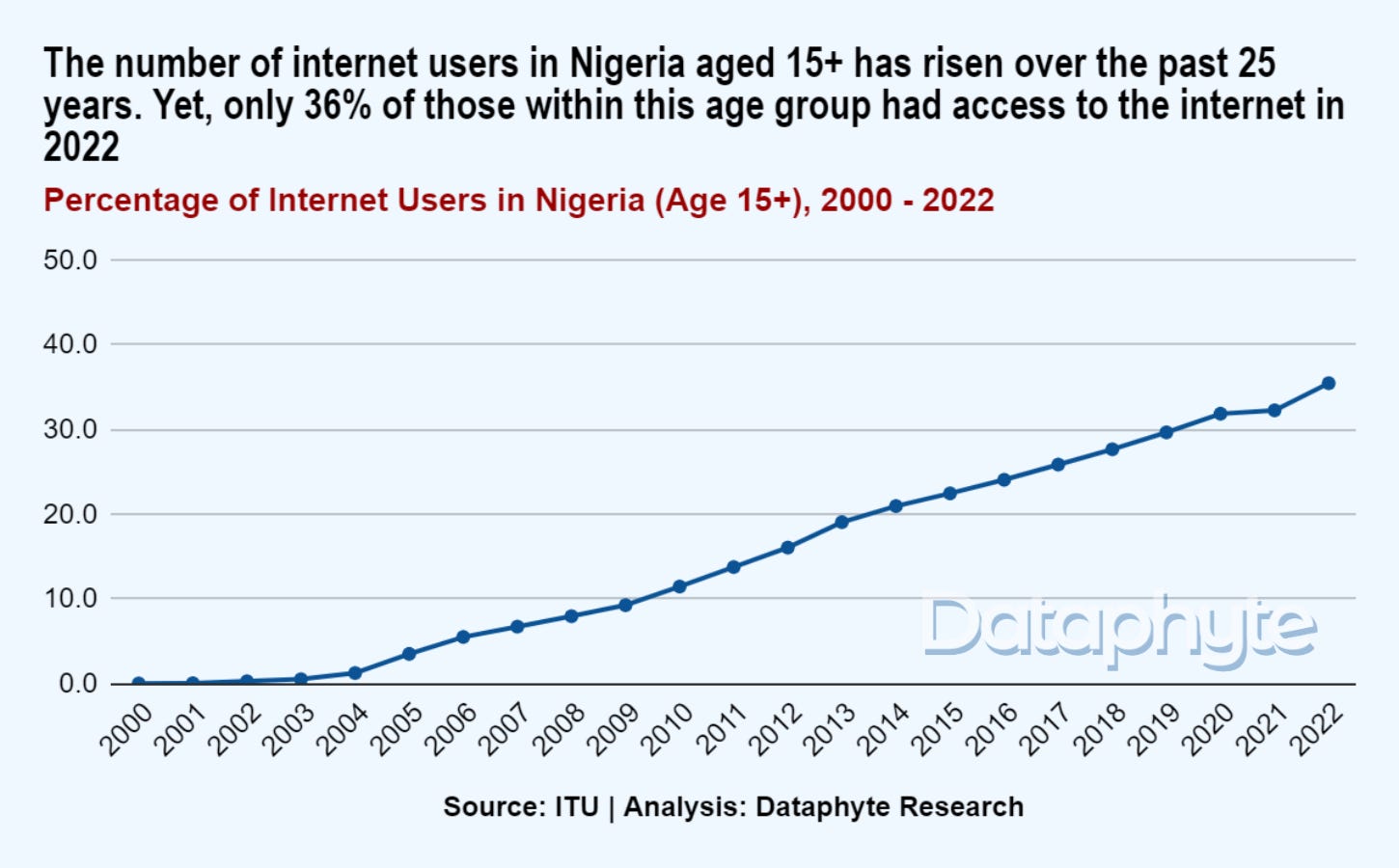
In Nigeria, the number of internet users aged 15+ has risen over the past 25 years. Yet, only 36% of those within this age group had access to the internet as of 2022.
Internet usage is often linked to a country's level of development because of its ability to drive novel and innovative solutions to global challenges and boost growth through exposure to digital technologies and information.
Increasing use of digital technologies and the adoption of artificial intelligence could hasten progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). However, limited internet access and scant ICT infrastructure can hinder young people from exploring emerging opportunities in digital technologies.
According to the IMF’s AI Preparedness Index, Nigeria’s digital infrastructure and regulations do not match up with the capacity of its human capital and innovation.
This informs why the country lags behind, with other Sub-Saharan African countries, with an index score of 0.34, one of the lowest in the world, and below the world average of 0.47.
Globally, a major digital infrastructure challenge is internet connectivity. About 2.6 billion people, or 33% of the world’s population, are unconnected to the internet as of 2023.
In the same period, 93% of people in high-income countries had internet access, compared to just 27% in low-income countries, a slight increase from 24% in 2022. This gap in digital penetration highlights the significant digital divide between high-income and low-income countries and regions.
The countries with the highest levels of digital penetration are in the high-income group, while those with the lowest levels are in the low-income group.
Although various factors affect a country's productivity, economic growth, and income level, leveraging new technologies and digital assets can significantly boost overall growth.
Progress: Youth Development
A country's robust growth depends not only on internet access and strong ICT infrastructure but also on the level of investment it makes in empowering its youth in key areas like education, employment, peace and security, as well as equality and inclusion.
By ensuring access to quality education, employment opportunities, and leadership platforms, young people are equipped with the resources needed to build a brighter future.
Nigeria's performance in youth development initiatives and overall growth lags behind the average score across the five regions of the world.
Over the past 13 years, Nigeria has performed low in six key areas critical to its youth development. This pattern reflects the country's efforts in implementing initiatives and programs that offer quality education and employment opportunities for its over 46 million youth aged 14 to 24 has yielded little returns.
The Youth Development Index (YDI) tracks a country’s progress on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) associated with youth development.
It measures a country’s effort towards enhancing the status of young people, empowering them to build on their competencies and capabilities for life and enabling them to contribute to and benefit from a politically stable and economically viable environment, ensuring their full participation as active citizens in their countries.
The UN World Youth Report 2020 highlighted that frontier technologies are fuelling structural transformations in societies and economies globally through digitisation and automation and young people, often early adopters of emerging technologies, are well-positioned to leverage these innovations to make a significant impact.
Clicks: Digital Pathways
The rapid advancement and spread of emerging and frontier technologies could potentially widen the digital divide and deepen existing inequalities. Therefore, it is increasingly vital to implement policies that ensure universal and equitable digital access, as the risk of leaving certain groups behind continues to grow.
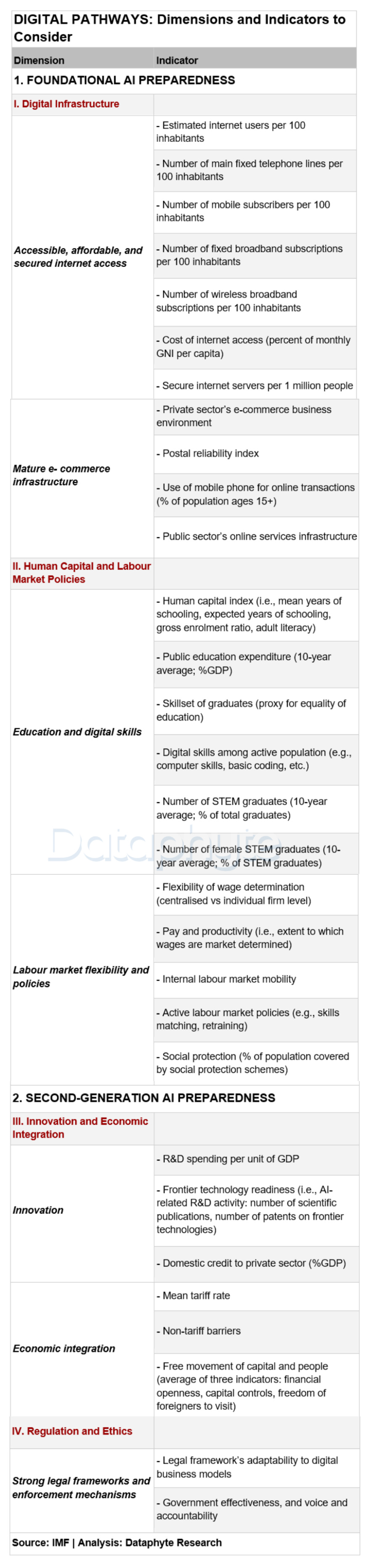
Finding a pathway for Nigeria and indeed its Sub-Saharan African neighbours, whose youth need the digital pathways to sustainable development the most, requires policymakers to assess and improve upon these vital metrics of digital advancements:
The UN Secretary-General noted that “Young people are leading the charge in digital adoption and innovation, with three-quarters of those aged 15 to 24 using the internet in 2022, a rate higher than other age groups. However, disparities persist, particularly in low-income countries and among young women, who often have less access to the internet and digital skills compared to their male counterparts.
While there is an urgent need to enhance digital inclusion, youth are largely recognized as “digital natives,” using technology to drive change and create solutions. As the 2030 deadline for the SDGs approaches, the role of young people in digital innovation is essential for addressing global issues.”